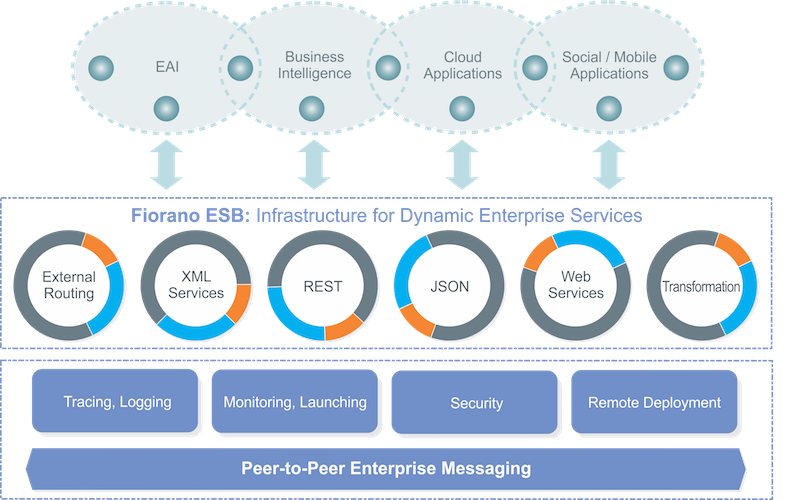
An ESB acts as a high speed expressway for data flow in an enterprise, enabling seamless communication among mutually interacting software applications. Fiorano ESB obviates point-to-point integration efforts and integrates heterogeneous applications, databases, cloud and other systems streamlining the complex architecture of an enterprise. Organizations can deploy the light-weight but powerful and scalable Fiorano ESB as their IT infrastructure backbone to enable real-time information across the enterprise.
| Document Download | |
Technical Architecture
The Fiorano ESB implements a brokered, peer-to-peer (often referred to as super peer) system architecture, which combines the management benefits of centralized hub-and-spoke systems with the performance benefits of fully distributed peer-to-peer systems, while avoiding the particular disadvantages of both of these individual approaches. The figure illustrates the Fiorano ESB brokered peer-to-peer architecture.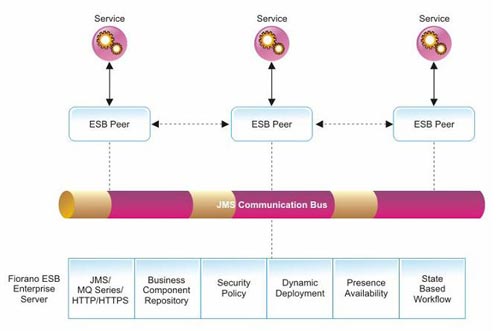

Particular benefits of the Fiorano ESB system architecture include:
- Enterprise Class Backbone: Underlying the ESB architecture is an enterprise-class, standards-based messaging backbone which provides secure and reliable communications between any number of applications and distributed integration processes across the enterprise. Using Fioranos unique distributed peer-to-peer JMS implementation, the backbone allows distributed integration processes and composite applications to scale to meet the requirements of the most demanding global enterprise networks.
- Efficiency: ESB peers at the end-points of the network allow distributed microservices to exchange events concurrently, enabling all of the parallelism in an integration process to be exploited. For instance, an order management system in a manufacturing plant can check its inventory status even as the sales-force management system is updating the order database. Data transformations and other computations required by distributed integration processes are performed concurrently at the end-points of the network.
- Unbounded Scalability: With dispersed computation and parallel message-flow between nodes, ESB peers scale naturally and seamlessly with the addition of new peer nodes and Enterprise microservices across the network.
- Ease of Administration: In a Fiorano ESB network, operations such as event-handling, security authentication and administration are performed by centralized servers. ESB peers at the end-points of the network are easily administered via tools connected to the centralized ESB Enterprise Server.
Fiorano’s brokered peer-to-peer architectural approach thus combines the benefits of both peer-to-peer systems and hub-and-spoke systems in a single cohesive architecture for a scalable enterprise backbone.
Key Features
Fiorano ESB is an Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) built on a MicroServices architecture that enables enterprises to integrate applications and processes in real-time with a federated bimodal approach to integration. This unique architectural design attributes a host of features to Fiorano ESB:
Distributed Services Architecture
- Message-Driven Microservice Model
Defines a coarse-grained, message-driven model for Enterprise microservices enabling each microservice to execute as an independent entity that is not tied into the context of execution until runtime, simplifying the componentization of existing Web Services, Database applications, Legacy, J2EE and .NET software assets, enhancing their reuse within event-driven business processes and automatically maximizing the parallelism concurrency within each business integration process. - Distributed, Dynamic Deployment and Management
Enables microservice deployment across the ESB infrastructure from any centralized location, allowing each individual microservice to be independently configured, managed, updated and redeployed without disrupting other services or processes. - Event-Process Orchestration
By enabling message-flows between distributed microservices to be set up dynamically by the underlying middleware, allows the logical process design to be mapped directly to physical services distributed across the ESB, empowering non-technical “citizen integrators” to compose, deploy and modify simple business processes. - Lifecycle Management and Versioning
Configuration management of labeled microservices and event-processes allowing controlled deployment across network end-points together with automatic transitions, with customizable service and process profiles, across the software lifecycle (development, QA, staging, production). - Support for multiple protocols and transports
Allows users to choose the transport used for event-flows between distributed microservices at runtime, providing the flexibility to use multiple transports and protocols across any distributed event-process.
Enterprise-Class, Peer-to-Peer Communications Backbone
- Unbounded Performance and Scalability
Peer-to-peer messaging obviates the need for events to traverse a central hub, enabling concurrent message-flows between distributed microservices and exploiting all available parallelism within distributed integration processes; effectively reuses hardware resources at network end-points, further reducing costs of operation. - Service-Level Failover and 24x7x Forever Availability
Enables failover instances of microservices to be dynamically deployed on remote ESB nodes based on multiple triggers, creating self-healing application networks and ensuring continuous availability under all operating environments. - Guaranteed message delivery
Ensures all messages within integration processes are reliably delivered to their destinations over a standards-based JMS API, with support for multiple additional protocols, without the need for applications to manage data retransmissions. - REST and Web Services Support
Implements REST, WSDL, SOAP and UDDI standards, enabling easy and reliable and secure integration of Web-services into message-driven integration processes. - Comprehensive Security
Provides a flexible framework for authentication, authorization and encryption, with support for J2EE, LDAP and other security standards, adapting to a wide range of federated enterprise security policies.
ESB Generic Services, Tools and Adapters
- Distributed Intelligent Routing
Enables dynamic changes to be seamlessly incorporated into running business processes by automatically routing events between distributed microservices on the ESB, with external control over route-changes; obviates single points of failure due to inherently parallel operation over distributed ESB infrastructure. - Monitoring, Logging and Auditing
Supports asynchronous notifications of critical errors in event processes, with dynamic tracing, logging, auditing and monitoring of messages, documents and services. Dynamic event-interception enables debugging of live event-flows across the ESB network, further reducing development/deployment time. - Multi-Language Support
Provides APIs for microservice-development in multiple languages including Java, C, C++, COM, C# (.NET), Visual Basic and various scripting languages, creating a true multi-language, multi-platform enterprise backbone. - XML Transformations
Supports sophisticated XSLT transformations, including EDI-XML, Database-XML and others, with pluggable external transformation engines; Enables semantic verification of event-process via XSD/DTD port matching. - Adapters and Pre-built Microservices
Ships with a rich set of pre-built enterprise microservices that allow over 70% of integrations to be implemented “out of the box”, with no additional programming; Key Services include adapters to all popular relational databases, files, Messaging Middleware (MQSeries, JMS, MSMQ, others) , WebServices, EJB, FTP, HTTP(S), SMTP, POP3 and more.

